By Cheri Stockhausen, Product Application Manager
An emulsifier is an agent that enables removal of excess post emulsifiable penetrant on part surfaces with water. Proper emulsification and rinse times allow removal of excess surface penetrant while any penetrant in discontinuities is not removed.
Unlike water washable penetrants, post emulsifiable penetrants do not contain surfactants, emulsifying agents, in their formulas. Post emulsifiable penetrants resist removal from discontinuities during the water rinse step because of the lack of surfactants in their formulas. However, an emulsifier is required to remove excess post emulsifiable penetrant from the part surface during the penetrant removal step.
Post emulsifiable penetrants (Methods B, C, and D) require either solvent removers (Method C) or emulsifiers (Methods B and D) to remove the excess penetrant from the part surface. Unlike water washable penetrants (Method A), post emulsifiable penetrants will not rinse from part surfaces with water alone. An emulsifier is required for Methods B and D penetrant processes.
There are two types of emulsifiers: Lipophilic and Hydrophilic.
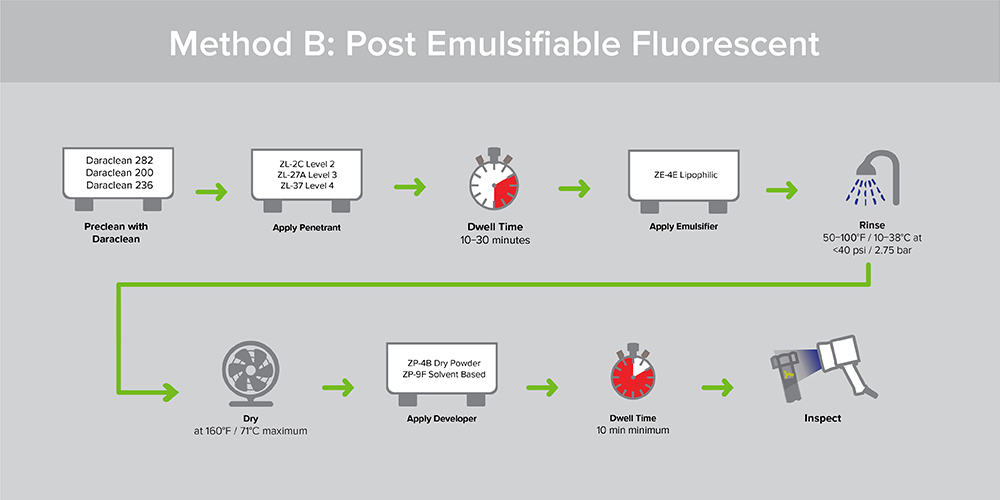
Lipophilic emulsifiers combine with post emulsifiable oil- based penetrants. The resultant emulsifier-penetrant combination can be removed from a part surface by water spray. The lipophilic emulsifier works primarily by diffusion into the post emulsifiable penetrant. Lipophilic emulsifiers are supplied in a ready to use form by the manufacturer. No pre-rinse step takes place. After the penetrant dwell time is completed, lipophilic emulsifier is usually applied by dip, and then the lipophilic emulsifier drains from the parts. The emulsification and drain step is timed to prevent over emulsification and possible removal of penetrant from discontinuities. Parts go through a water rinse immediately after the emulsification time.
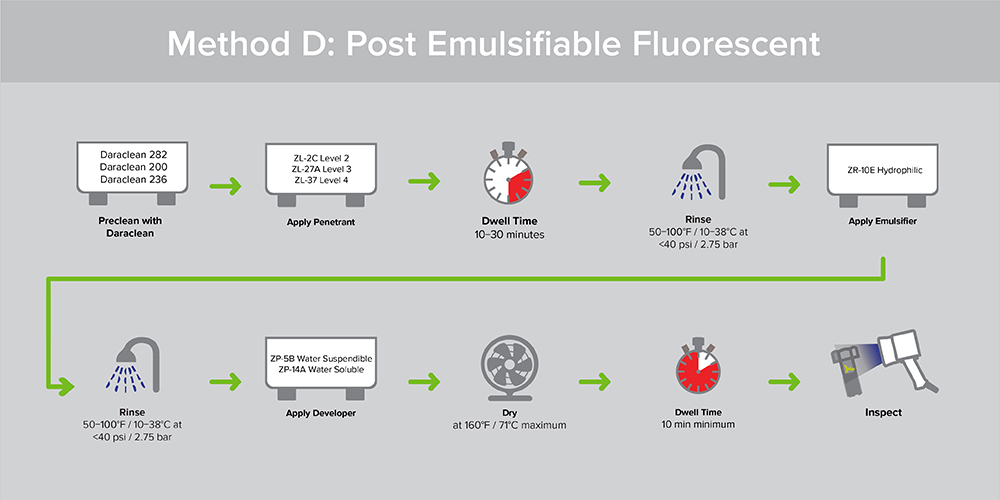
Hydrophilic emulsifiers are supplied as a concentrate. Hydrophilic emulsifiers are diluted with water following the manufacturer’s recommendation. Hydrophilic emulsifiers work by detergent action. After the penetrant dwell time, parts are pre-rinsed with water before application of the hydrophilic emulsifier. Parts are immersed in a mildly agitated tank of hydrophilic emulsifier. Hydrophilic emulsifier may also be applied to parts by spray. With spray application of hydrophilic emulsifier, the pre-rinse step is usually omitted. The hydrophilic emulsification step is followed by a final water rinse.
Published July 24, 2018
Updated February 5, 2019
The Magnaflux team is happy to assist you with your nondestructive testing needs. Please opt-in to Tracking cookies to use the contact form by clicking Cookie Settings and updating your preferences to complete our contact form. If you do not wish to opt in, you can connect with us at support@magnaflux.com or call us at +1-847-657-5300
155 Harlem Avenue
Glenview, IL 60025, USA
Telephone: +1 847-657-5300
Contact Magnaflux Customer Service